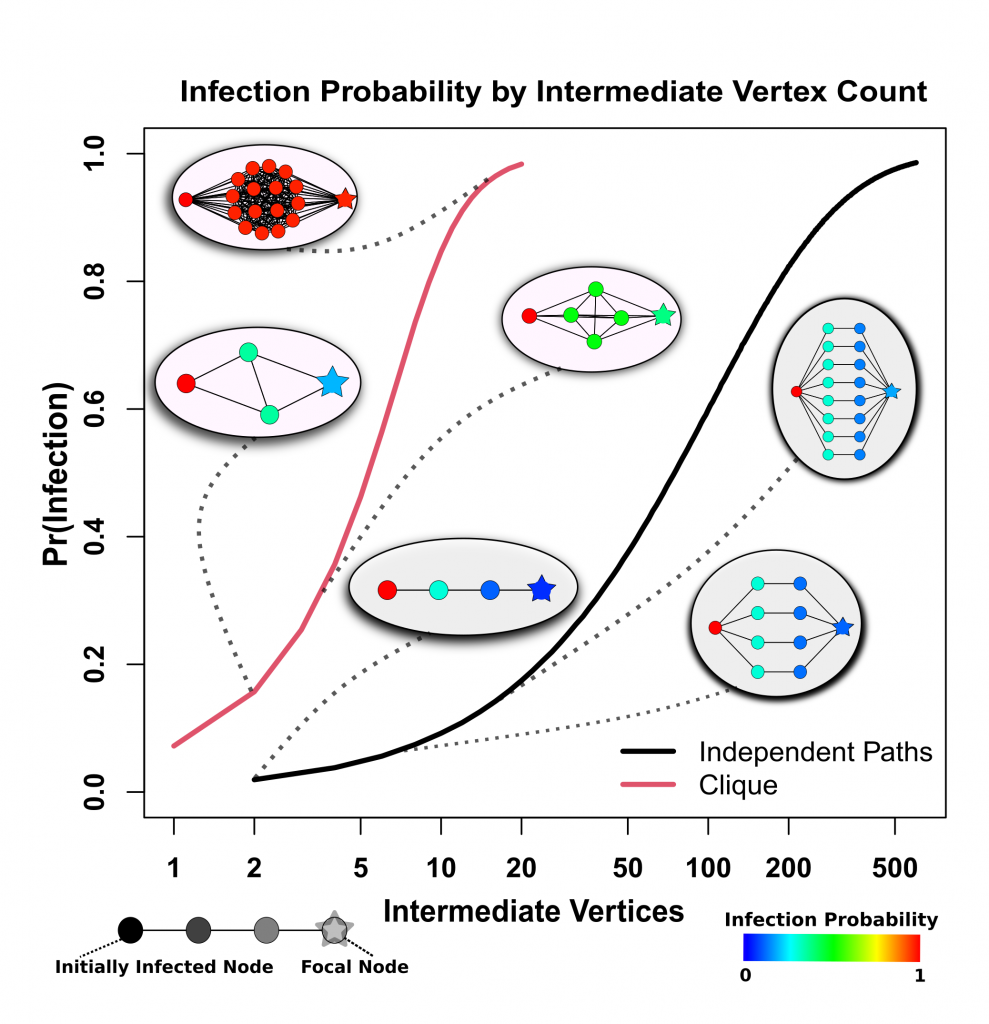
California Exodus? A Network Model of Population Redistribution in the United States
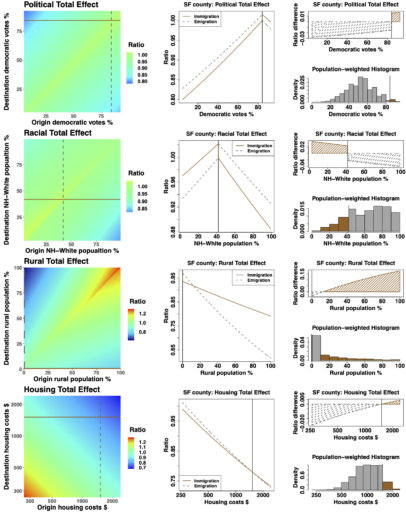
The California Exodus, where droves of population are leaving California and settling in other U.S. states, has recently received broad media coverage, but less attention in scientific research. In a recent paper published in Journal of Mathematical Sociology, NCASD researchers Peng Huang and Carter Butts analyze the population redistribution pattern in the United States. They […]
California Exodus? A Network Model of Population Redistribution in the United States Read More »